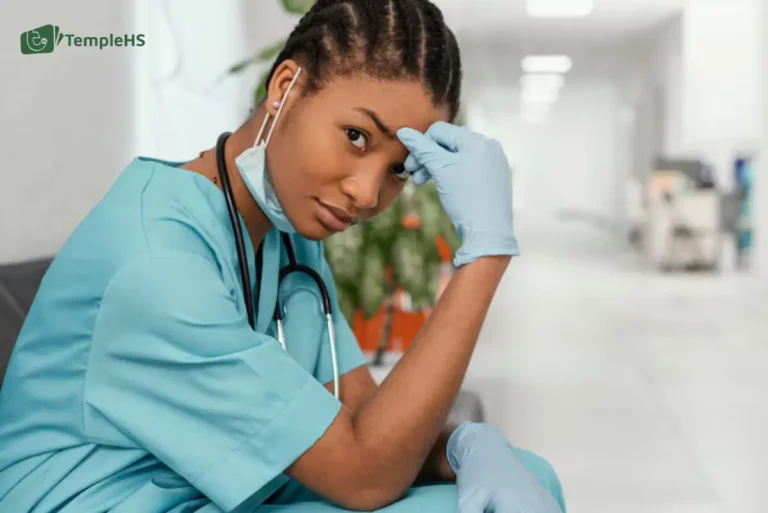
Nurse burnout is a serious issue that affects many healthcare professionals today. It occurs when nurses face overwhelming stress, leading to physical, emotional, and mental exhaustion. This impacts their well-being and the quality of care they can provide to patients. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and implementing effective prevention strategies are crucial steps in addressing this challenge. By focusing on these aspects, we can support our nurses and ensure they have the resources and environment needed to thrive in their vital roles.
This article explores the key aspects of nurse burnout, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, and the best strategies for prevention, with the aim of supporting nurses in their vital roles and ensuring the well-being of both healthcare workers and patients.
Definition and Prevalence of Nurse Burnout
Nurse burnout is a state of physical, emotional, and mental exhaustion caused by prolonged exposure to stressful working conditions. Unlike stress, which can be temporary and situation-specific, or depression, a broader mental health condition, burnout specifically relates to the work environment and its demands.
Burnout among nurses is characterized by three main components: emotional exhaustion, depersonalization (where nurses may become cynical about their work and patients), and a reduced sense of personal accomplishment. Research across various countries indicates that nurse burnout is a significant issue, with studies showing high levels of burnout symptoms among nursing professionals. For instance, surveys have found that a considerable percentage of nurses report experiencing symptoms of burnout, highlighting the global scale of the problem.
What Are the Causes of Nurse Burnout?
1. Long Working Hours
Nurses often face shifts that extend well beyond the standard eight hours, sometimes working up to 12 hours or more without sufficient breaks. This excessive workload can lead to physical fatigue, making it hard for nurses to recover between shifts. The continuous cycle of long hours contributes to burnout by not only wearing down the body physically but also reducing the time available for personal care, rest, and social activities, which are essential for mental health and well-being.
2. High-Stress Environments
The nature of nursing involves working in environments where the stakes are high, and the pressure is constant. Nurses must make quick decisions in emergency situations, manage complex patient care needs, and navigate the dynamics of healthcare teams. This continuous exposure to high-stress situations can lead to emotional exhaustion. The stress of constantly being in such an intense environment wears down resilience and can lead to feelings of being overwhelmed, a key component of burnout.
3. Emotional Demands of Patient Care
Forming emotional connections with patients is an inherent part of nursing. While these relationships can be rewarding, they also carry an emotional toll, especially when nurses witness suffering, trauma, and death. The cumulative effect of these emotional experiences can lead to compassion fatigue, where nurses begin to detach from their feelings as a coping mechanism, contributing to burnout by making them feel less engaged and more cynical about their work.
4. Staffing Shortages
With not enough nurses to meet the demand in many healthcare settings, the workload on individual nurses increases significantly. This situation leads to a scenario where nurses have to care for more patients than is safely manageable, reducing the quality of care and increasing the pressure and stress on the nurses. The feeling of being unable to provide adequate care due to these shortages can be demoralizing, heightening the risk of burnout.
5. Lack of Administrative Support
When nurses feel unsupported by management, especially regarding their working conditions, patient care concerns, or professional development, it can lead to a sense of isolation and frustration. Effective support systems within healthcare settings are crucial for addressing the challenges nurses face. Without this support, nurses may feel their needs and concerns are not taken seriously, further contributing to the emotional and mental strain that leads to burnout.
Symptoms and Effects of Burnout
1. Emotional Exhaustion
Nurses feeling emotionally drained and overwhelmed by their work is a key sign of burnout. This state results from the constant pressure and stress of nursing duties, leaving nurses feeling like they have no energy or enthusiasm left for their job or even for their personal life. Emotional exhaustion can lead to increased absenteeism, a desire to leave the profession, and a decline in mental health, manifesting as anxiety or depression.
2. Depersonalization
This symptom involves a sense of detachment from the job and patients. Nurses may start to see their patients as tasks rather than individuals needing care. This detachment can harm the quality of patient care, as nurses might become less empathetic, less engaged, and more mechanical in their work. It also affects the nurse’s job satisfaction and their ability to connect with colleagues and patients.
3. Reduced Sense of Personal Accomplishment
Nurses experiencing burnout often feel like they are not achieving anything worthwhile in their job. Despite their hard work and dedication, they might believe that their efforts do not make a difference, leading to feelings of inadequacy and failure. This can decrease motivation, lower job satisfaction, and increase thoughts of leaving the profession.
4. Effects on Mental and Physical Health
Burnout not only affects nurses mentally, by increasing the risk of depression and anxiety, but also physically. Nurses may experience symptoms like headaches, fatigue, insomnia, and gastrointestinal problems. The stress associated with burnout can lead to higher susceptibility to illnesses due to a weakened immune system, further exacerbating the nurse’s condition and possibly leading to more time off work.
5. Job Performance and Patient Care Quality
The quality of care that nurses provide can decline significantly due to burnout. Mistakes may become more common, and the attention to patient needs may decrease, affecting patient satisfaction and outcomes. Burnout can lead to a lack of focus, reduced efficiency, and a decrease in the quality of patient interaction, ultimately impacting the overall performance of healthcare services.
Impact of Nurse Burnout on Healthcare Systems
Nurse burnout has significant impacts on healthcare systems. It leads to increased turnover rates, as nurses often leave their jobs seeking relief from the stress, resulting in staffing shortages. These shortages put additional pressure on remaining staff and can delay patient care. Recruiting and training new nurses add to healthcare costs, making the system less efficient and more expensive to operate. Furthermore, burnout affects the quality of care nurses can provide. They may make more mistakes or not give patients the attention they need, which can compromise patient safety and satisfaction. The overall effect is a strained healthcare system struggling to maintain high standards of care while managing the wellbeing of its workforce.
Prevention Strategies for Nurse Burnout
1. Self-Care Techniques
Nurses should prioritize self-care to prevent burnout. This includes activities that promote physical health, like regular exercise, a balanced diet, and enough sleep, as well as mental health activities such as meditation or hobbies. By taking care of their own well-being, nurses can better manage stress and maintain their energy levels. This approach helps in coping with the demanding nature of their work and supports overall resilience.
2. Stress Management
Effective stress management is crucial for nurses. Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, mindfulness, and yoga can reduce stress levels. Regular participation in these activities helps nurses stay calm and focused, especially in high-pressure situations. Additionally, time management skills can help prioritize tasks and reduce work-related stress, making their workload more manageable.
3. Professional Support
Seeking professional support, like counseling or therapy, can be beneficial for nurses dealing with burnout. Professional therapists can provide strategies to cope with stress, work-related challenges, and emotional distress. Support groups for healthcare professionals can also offer a space to share experiences and solutions, fostering a sense of community and mutual support.
4. Supportive Work Environments
Organizations can play a key role in preventing nurse burnout by creating supportive work environments. This involves acknowledging the hard work of nurses, providing regular feedback, and ensuring that nurses feel valued and heard. Establishing a culture of support and respect within healthcare settings can significantly reduce stress and improve job satisfaction.
5. Staffing Models and Mental Health Resources
Implementing staffing models that promote work-life balance is essential. Adequate staffing reduces the workload on individual nurses, allowing for better patient care and reducing the risk of burnout. Providing access to mental health resources, such as counseling services and stress management workshops, supports nurses’ mental well-being, helping them to cope with the demands of their profession.
Conclusion
Addressing nurse burnout is essential for the health and well-being of both nurses and the patients they care for. By understanding the causes and symptoms, we can better identify those at risk and take action to prevent burnout before it starts. Effective prevention strategies, including support from healthcare organizations, stress management training, and creating a positive work environment, can make a significant difference.