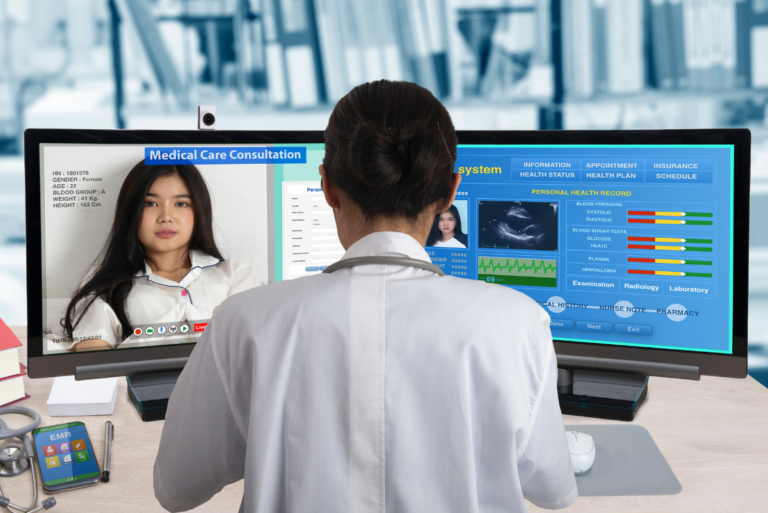
Patient records are more than mere documents; they are vital tools in the continuum of care. They allow for a cohesive understanding of a patient’s medical history, treatment plans, and health outcomes. By implementing efficient record management practices, healthcare providers can improve the quality of care, enhance patient safety, and streamline administrative processes.
However, many struggle with organizing and accessing patient information quickly and accurately. So, this post will discuss strategies for managing patient records more efficiently. We’ll cover the essentials, from digitization to maintaining privacy and security, offering practical solutions that can be implemented in various healthcare settings.
Methods for organizing, storing, and retrieving patient information
Organizing Patient Information
1. Categorization
Organize patient records into clear categories such as personal information, medical history, treatment plans, and billing details. This makes it easy to locate specific types of information quickly. For digital records, use consistent naming conventions and folder structures. For physical records, use labeled dividers and color-coding systems.
2. Chronological Ordering
Maintain records in chronological order to track the progression of a patient’s medical history and treatment. This method is particularly helpful for quickly reviewing a patient’s recent medical interactions or long-term health trends.
3. Standardization of Forms and Templates
Use standardized forms and templates for both digital and physical records. This consistency ensures that all necessary information is captured uniformly, making it easier to compare and contrast patient records when necessary.
Storing Patient Information
1. Digital Storage Solutions
Utilize electronic health record (EHR) systems for digital storage, which offer robust data organization, security, and backup options. Cloud-based solutions can provide additional benefits such as remote access and reduced physical storage needs.
2. Physical Storage Security
For physical records, secure filing systems such as locked cabinets or dedicated record rooms are essential. These should be in a controlled environment to protect against environmental damage and ensure only authorized personnel have access.
3. Backup and Redundancy
Regularly back up digital records to prevent data loss due to system failures or cyber incidents. For physical records, having a digitized backup is advisable for added security and ease of retrieval.
Retrieving Patient Information
1. Search Functionality in EHR Systems
Utilize the search functionalities of electronic health record systems to quickly locate specific records or information. These systems often allow searches by various fields such as patient name, date of birth, or specific medical conditions.
2. Indexing System for Physical Records
For physical records, maintain an updated index or cataloging system to track the location of each file. This system can be as simple as a spreadsheet or a dedicated database, depending on the size of the practice.
3. Regular Audits and Updates
Conduct regular audits of both digital and physical records to ensure that all information is filed correctly and is readily retrievable. This process helps identify and correct any organizational issues, ensuring efficient retrieval of records when needed.
Common Challenges Faced by Medical Facilities in Record Management
1. Data Security and Privacy
Ensuring the confidentiality and security of patient records is a significant challenge, particularly with the rise of cyber threats. Medical facilities must protect sensitive data from unauthorized access, breaches, and other security risks while complying with regulations like HIPAA.
2. Integration of Multiple Systems
Many healthcare facilities use a variety of software systems for different purposes, such as patient care, billing, and insurance. Integrating these systems to ensure seamless, error-free transfer of patient data can be a complex task.
3. Compliance with Regulatory Requirements
Maintaining compliance with ever-evolving healthcare regulations and standards is a continuous and resource-intensive task. This is especially true for adhering to the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), which sets strict standards for patient data privacy and security. Staying updated with changes in HIPAA regulations and other healthcare laws related to data retention and security is crucial. Failure to comply with these legal requirements can result in significant legal and financial repercussions for healthcare providers.
4. Managing Paper and Digital Records Simultaneously
Balancing digital and physical record-keeping poses challenges, especially for facilities transitioning to electronic records. Ensuring consistency, accuracy, and accessibility across both formats is complex.
5. Accurate and Timely Documentation
Ensuring that patient records are updated accurately and in a timely manner is crucial for effective care. Errors or delays in documentation can lead to misdiagnoses, inappropriate treatment plans, and other critical issues in patient care.
Use TempleHS for Effective Patient Record Management
TempleHS is a Medical Practice Hosting Solution that can effectively address documentation challenges for solo private practitioners. With its integrated platform, TempleHS simplifies data entry and record-keeping, reducing the likelihood of errors and delays in documentation. Its user-friendly interface allows practitioners to update patient records quickly and accurately, ensuring timely and correct information is always available.
The system’s robust security measures safeguard sensitive patient data, addressing data security and privacy concerns. Additionally, TempleHS facilitates compliance with regulatory requirements by incorporating the latest standards and guidelines into its system. This ensures practitioners are always in line with legal obligations without investing additional time or resources into compliance research.
Conclusion
Streamlining patient record management is not just about adopting new technologies; it’s about creating a system that works seamlessly for healthcare professionals and patients. By implementing the methods discussed, such as digitization, regular audits, and employee training, healthcare providers can improve the accuracy and accessibility of patient records. This, in turn, leads to better patient care, enhanced privacy, and compliance with legal requirements. Start small, focus on one area at a time, and gradually build a more efficient, responsive patient record system.