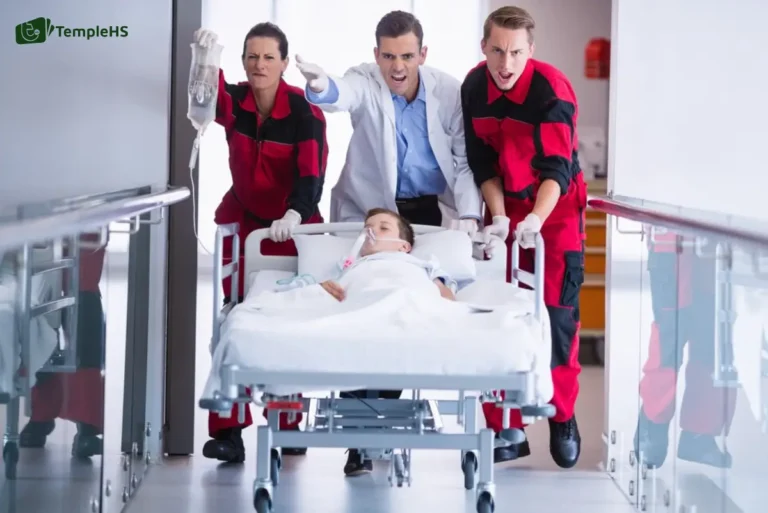
In healthcare, unforeseen emergencies are inevitable. Efficiently managing these urgencies is essential for delivering timely, high-quality care and maintaining patient trust. Developing a structured approach for handling emergency appointments ensures that healthcare practitioners can respond effectively to sudden demands without disrupting scheduled services.
This post will cover best practices for managing emergency appointments, helping healthcare practitioners provide swift and organized responses to urgent patient needs.
Best Practices for Healthcare Practitioners Facing Unforeseen Urgencies
1. Establish Clear Triage Protocols
Setting up a standardized triage system helps determine the urgency of incoming cases, allowing practitioners to prioritize patients based on their condition. Develop clear protocols for categorizing emergencies, from life-threatening situations to urgent but non-critical needs. Train all front-line staff to assess patient symptoms quickly and accurately, ensuring that true emergencies receive immediate attention.
2. Reserve Time Slots for Emergency Appointments
Designate specific time slots throughout the day for emergency appointments. This allows flexibility to accommodate unforeseen urgencies without disrupting the entire schedule. Reserving one or two slots in the morning and afternoon can create a buffer that allows for unexpected cases. If no emergencies arise, these slots can be used for follow-up appointments or same-day scheduling requests.
3. Use a Digital Appointment Management System
A digital appointment system can streamline scheduling, allowing you to adjust in real-time for emergencies. Look for systems with features like automated reminders, open slot notifications, and real-time schedule updates. TempleHS is a great asset for these. A robust system can help prioritize emergency appointments, notify patients of delays, and optimize workflow by dynamically rescheduling non-urgent visits when emergencies arise.
4. Develop a Clear Communication Plan
Effective communication with patients is crucial in emergency situations. Train staff to communicate clearly and compassionately with patients when rescheduling or adjusting non-urgent appointments. Use multiple communication channels—such as phone, text, and email—to keep patients informed about delays or schedule changes due to emergency cases. Maintaining transparency helps manage expectations and reduces frustration among patients affected by unforeseen delays.
5. Train Staff for Flexibility and Quick Decision-Making
In emergencies, quick decision-making can make a difference. Train staff to be flexible and to adapt to changes in real-time. Create protocols that empower them to rearrange the schedule as needed, call in additional practitioners if necessary, and handle intake paperwork promptly. Providing guidelines for handling varying types of emergencies will help staff make decisions swiftly and accurately.
6. Prioritize Documentation and Follow-Up
Document each emergency appointment thoroughly to maintain accurate records and to inform future care. Post-emergency, schedule follow-up appointments as needed to ensure continuity of care for the patient. Clear documentation also helps avoid oversights in patient care, and it keeps all healthcare providers in the loop, improving collaboration and reducing the likelihood of information gaps.
7. Implement a Backup Resource System
Establish a network of backup resources that can help accommodate unexpected patient loads. This could involve on-call staff, partnerships with nearby urgent care facilities, or pre-established relationships with specialists for referrals. Having backup resources in place helps ensure that critical patients receive the necessary care promptly, even during peak times or staff shortages.
8. Conduct Regular Reviews of Emergency Handling Protocols
Periodic reviews of emergency management practices help identify areas for improvement. Hold debriefs after emergency situations to assess what went well and what could have been handled more effectively. Regular reviews help refine protocols, keep the team prepared for future urgencies, and improve the overall efficiency and effectiveness of emergency care.
Conclusion
Managing emergency appointments effectively requires a combination of structured protocols, flexible scheduling, clear communication, and continuous improvement. By implementing these best practices, healthcare practitioners can respond to unforeseen urgencies with confidence, providing timely care without compromising service quality for scheduled patients. With a proactive approach, practices can ensure they are equipped to handle emergencies smoothly, enhancing patient trust and care outcomes.